Sftp Linux Permission Denied Please Try Again
Introduction
The SSH Permission denied error appears subsequently permission-related settings are modified on the SSH server. Usual scenarios include a new parcel installation or the creation of new users.
In this tutorial, you will acquire how to troubleshoot the SSH Permission denied error and reconnect to your SSH server.
Prerequisites
- SSH client on the local machine and SSH server on the remote system
- A user account to access the remote server (for password-based login)
- A user business relationship withsudo orrootprivileges
What is Causing SSH Permission Denied (publickey,gssapi-keyex,gssapi-with-mic)?
The SSH Permission denied error appears when trying to SSH into a server:
Permission denied (publickey,gssapi-keyex,gssapi-with-mic) 
Post-obit the Permission denied argument, the bracket contains the attempted hallmark methods that failed at the initiation of the connexion. The error suggests that the public fundamental is the issue, which is misleading.
Ane reason for the error may be sshd_config , the file that contains SSH server configuration. The other possibility is that the authorized_keys file has insufficient permissions. This file contains the list of public keys for the clients allowed to SSH into the server. Consequently, the system's inability to read from the file results in the Permission denied mistake.
How to fix SSH Permission denied
Both solutions contain steps yous need to perform on the server-side. Start by opening the terminal on your server and proceed with one of the solutions below.
Solution 1: Enable Password Authentication
If you desire to utilize a password to access the SSH server, a solution for fixing the Permission denied error is to enable password login in the sshd_config file.
To practise this, open up the file in a text editor. This instance uses the nano editor:
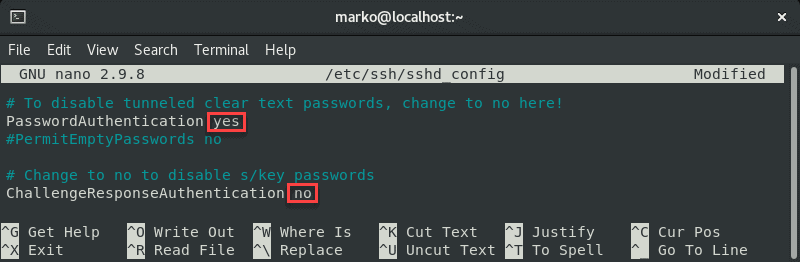
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config In the file, find the PasswordAuthentication line and make sure information technology ends with yeah .
Find the ChallengeResponseAuthentication option and disable it by adding no .
If lines are commented out, remove the hash sign # to uncomment them.
Save the file and exit.
Restart the SSH service past typing the following control:
sudo systemctl restart sshd Solution ii: Change File Organisation Permissions
Using the password-based login as the SSH hallmark method is not recommended due to security concerns. Therefore, the post-obit solution may exist preferable since it troubleshoots the public cardinal authentication method.
First, open up the sshd_config file using a text editor:
sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_config In the file, make certain the post-obit options are set every bit follows:
PermitRootLogin no PubkeyAuthentication yes 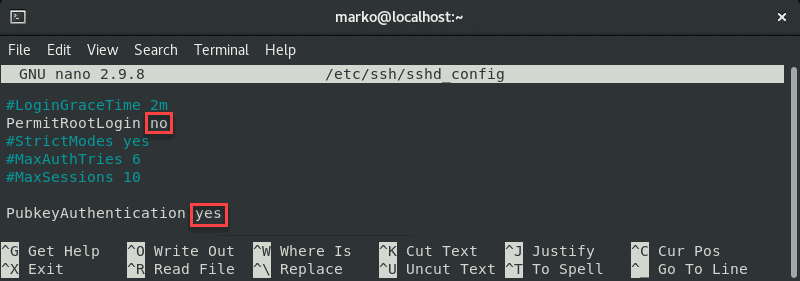
Note: The steps in a higher place are considered best security practices. If you need to use root login, set up the relevant line to yeah .
Annotate out the GSSAPI-related options by adding the hash sign at the outset of the line:
#GSSAPIAuthentication yes #GSSAPICleanupCredentials no 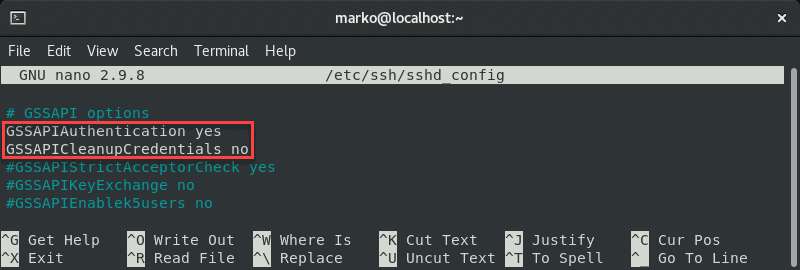
Also, brand sure the UsePAM line is gear up to yes :
UsePAM yes 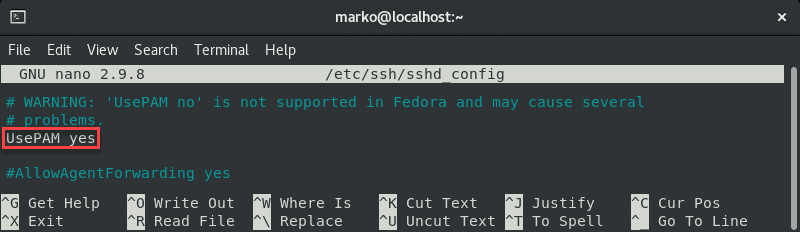
Salve the file and restart the sshd service:
systemctl restart sshd Now navigate to your home folder and bank check the permissions:
ls -ld 
If your owner permissions are not set up to read, write, and execute ( drwx------ ), apply the chmod command to change them:
chmod 0700 /domicile/[your-username] Now go to the .ssh folder and recheck the permissions:
ls -ld 
This directory should also take read, write, and execute permissions for the file owner. To enforce them, use chmod again:
chmod 0700 /abode/your_home/.ssh The .ssh binder contains the authorized_keys file. Bank check its permissions with:
ls -ld authorized_keys 
The file owner should have read and write permissions. To fix them, use:
chmod 0600 /home/[username]/.ssh/authorized_keys Now try logging in with the key pair again. The output below shows a successful login attempt.
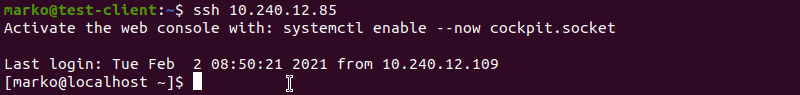
Conclusion
This tutorial covered the steps necessary to troubleshoot the SSH Permission denied (publickey,gssapi-keyex,gssapi-with-mic) error. By completing the steps in the guide, you should set up the mistake and successfully SSH into your server.
Was this article helpful?
Yes No
Source: https://phoenixnap.com/kb/ssh-permission-denied-publickey
Postar um comentário for "Sftp Linux Permission Denied Please Try Again"